Introduction
Peripheral nerve tumors can occur anywhere in the body. Most of them aren't cancerous ...
One in five women complain of bladder weakness at the gynaecologist`s office and at least one in six adults of both sexes suffers from an overactive bladder, making it generally one of the most common disorders across the board. Problems with the bladder and frequent urination severely restrict the personal activities and quality of life of those affected, even to the point of social isolation. But there is almost always a way out.
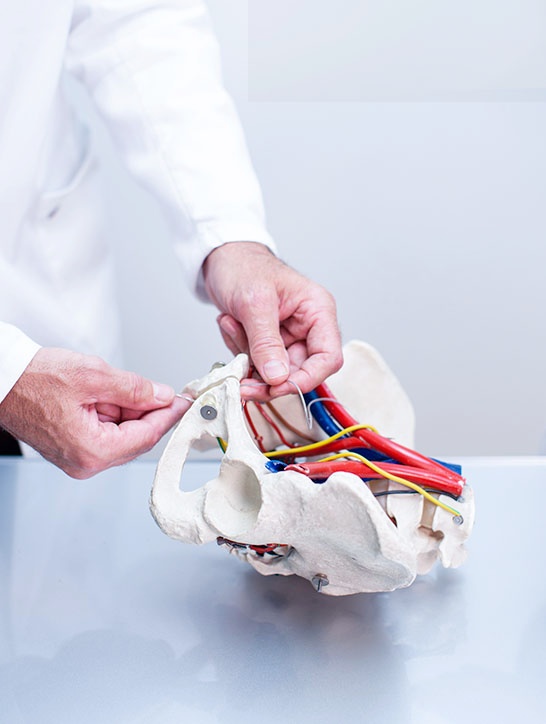



Electrical stimulation of the pelvic nerves is a treatment option for an irritable bladder, especially if it occurs in combination with urinary incontinence. It can be considered if, for example, behavioral therapy for an overactive bladder does not produce the desired results.
Genital nerve stimulation is a reversible therapy that can alleviate or even completely eliminate the symptoms. In a minimally invasive procedure, a microstimulator system, a few millimetres in size, is placed behind the pubic bone on the genital nerve by laparoscopy. Electrical stimulation of the urethra relaxes the bladder muscles. In this way, the overactivity of the bladder is reduced and, if present, urinary incontinence is controlled.
In addition to GNS therapy, which is based on stimulation of the genital nerve, the PN-Stim-LION method may also be appropriate. This focuses on the pudendal nerve, which is primarily responsible for controlling the bladder, rectum and sphincters.
Another common type is urge incontinence, which is characterized by a strong urge to urinate. Urge incontinence leads to repeated, involuntary tightening of the bladder muscles. Such disorders increasingly occur in connection with an overactive bladder - the so-called irritable bladder - interstitial cystitis, prostatitis, prostadynia or benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Urge incontinence manifests itself in a sudden, multiple and intense urge to urinate. This form of incontinence is the second most frequently diagnosed. Many women only suffer from urge incontinence if they are particularly under stress. The most common form of urge incontinence is the overactive bladder, also known as the "irritable bladder". In most cases, no cause can be found for this problem. In older people, however, it often develops as a result of diseases of the nervous system, such as Parkinson's disease, stroke, diabetes and others.
The irritable bladder is defined by a number of symptoms: an urge to urinate, with or without urge incontinence, mostly frequent and also at night. The main symptom is a frequent urge to urinate - the feeling of constantly having to go to the toilet, which the patient cannot control. Frequent urination" usually means more than eight toilet visits per day. Some patients also unintentionally lose urine (urge incontinence).
Overflow incontinence, also called overflow bladder, is accompanied by an overstretching of the urinary bladder. Those affected do not feel the urge to urinate, which warns them in good time. This inevitably leads to an overstretching of the bladder and usually to a backflow of urine into the kidneys, which carries with it the risk of kidney damage.
Urinary incontinence can also be caused by years of infrequent visits to the toilet or too long intervals between visits. In this case the overflow incontinence is so to speak trained.
Mixed urinary incontinence is a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
Pessaries, oestrogens
Vaginal inserts - so-called pessaries - to support the urethra can only temporarily eliminate incontinence. Vaginal oestrogens help the mucous membranes of the bladder and urethra, to remain pliable.
Surgical Methods
There are a number of surgical methods in which the pelvic floor is tightened and the urethra is raised again. Abdominal incision surgery has been completely replaced by vaginal or minimally invasive procedures. Loop operations are very straightforward interventions with excellent results. The basic prerequisites for these operations are:
It is strictly a case of stress incontinence
Loop operations must be strictly avoided in the case of irritable bladder (urge incontinence), overflow bladder and mixed form incontinence.
The complete emptying of the bladder (without abdominal pressing) has been confirmed by ultrasound. Otherwise, it would lead to an increasingly incomplete emptying of the bladder with the danger of urinary retention or a more and more overstretched bladder with subsequent slackening of the bladder.
Genital Nerve Stimulation - GNS Therapy
If loop surgery is not possible or successful, or a combination of bladder and bowel incontinence is present, genital nerve stimulation (GNS therapy) is the treatment of choice.
Through a small incision under the pubic hair, a microstimulator system a few millimetres in size is placed behind the pubic bone on the genital nerve by laparoscopy. A remote control stimulates the genital nerve, which reduces bladder overactivity and improves control of urinary incontinence. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia and takes less than 30 minutes. In addition to the positive effect on bladder function, stimulation of the genital nerve also improves sexual satisfaction and penile erection. The procedure is reversible and can be interrupted at any time by switching off or removing the device.
Behavioural therapy
In the case of an overactive bladder or irritable bladder, behavioural therapy is the first choice. This can include a change in dietary habits to see if less caffeine, alcohol and spicy foods reduce symptoms. A daily "bladder diary" is usually kept for this purpose in order to be able to check the frequency of bathroom visits. Changes in behaviour can include going to the toilet at certain times during the day and doing a Quick Flick Kegel exercise to relax the bladder muscle. Most patients do not get rid of their symptoms completely by changing their lifestyle habits. However, many have fewer symptoms due to this treatment.
Treatment with medication
Drug treatments - so-called anti-muscarins - do reduce the symptoms, but are only a second choice treatment option due to the fact that they often have troubling side effects such as a dry mouth, constipation, dry or itchy eyes, blurred vision, dyspepsia, urinary infections, urinary problems and cognitive dysfunction and may only be used in patients over 75 years with extreme caution. These side effects are often so difficult to tolerate, which leads to them being discontinued in 60% of all cases.
Botulinum Toxin A
Injections with botulinum toxin A in the bladder may be suggested as third treatment choice option.They come into question if the above therapies were unsuccessful or had too many side effects. Patients must be given comprehensive advice beforehand. Due to the changes in the bladder caused by the botulinum, the patient must be able to come to the practice for frequent follow-up checks and, if necessary, be able to undergo and perform self-catheterization. Patients must be given comprehensive advice beforehand. Since botulinum therapy requires a bladderoscopy (often under general anaesthesia) and this normally has to be repeated every 6 to 9 months for the rest of the patient's life, which can be difficult for patients to accept.
Genital Nerve Stimulation - GNS Therapy
The electrical stimulation of the pelvic nerves provides a treatment option for an irritable bladder, in particular if it occurs in combination with urinary incontinence. Genital nerve stimulation can alleviate or even completely eliminate the symptoms. Electrical stimulation of the urethra relaxes the bladder muscles. GNS therapy treats the irritable bladder and at the same time urinary incontinence, if present.
Through a small incision under the pubic hair, a microstimulator system a few millimetres in size is placed behind the pubic bone on the genital nerve by laparoscopy. A remote control stimulates the genital nerve, reducing bladder overactivity and improving urinary incontinence control. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia and lasts less than 30 minutes. In addition to the positive effect on bladder function, stimulation of the genital nerve also improves sexual satisfaction and penile erection. The procedure is reversible and can be interrupted at any time by switching off or removing the device.

Professor Marc Possover is one of the most incredible, rare professional, intellectual doctors whom i ever met.
I was lucky to be present at a difficult surgical oncological operation of one of my patients.
Dear Dr. Possover. We would like to thank you very much for the operation you performed in November 2014. Thanks to your excellent work we have become parents of two sons. Our family will always be grateful to you. Best regards.
For more than 4 years I suffered from a tearing pain in the pelvic floor and a strong irritable bladder. Oestopathy, urologists, acupuncture and a neurologist who wanted to send me to a rheumatologist could not help.
My name is Mrs. Liat Nadel, 51 years old, married and live in Israel. I was only 12 when my Endometriosis knocked on my door/life, but was actually diagnosed only 11 years later by mistake, "thanks" to an emergency surgery.
From the moment I walked into the consultation room and the Professor's initial response to my complaint I felt overwhelmingly at ease. For a healthcare professional to finally know exactly what your problem was but more importantly telling me he could fix the problem was like winning the lottery and he certainly delivered on his promise.
To help people in difficult situations to improve their quality of life has become his life's passion. Continuous research, decades of clinical experience and the focused determination to find a solution for previously unsolved medical problems, have enabled Prof. Possover to help often quite discouraged patients find release from their seemingly insurmountable problems.
Our team will take care of you
Neuropelveology is a medical discipline developed by Prof. Possover. It is based on the discovery of the pelvic nerves and includes the diagnosis of the diseases of these nerves by means of gynaecological examination methods and their treatment by means of laparoscopy.
Read moreWe will dedicate our expertise and know-how to help you find the solution that is right for you.
„As a cheerful, open and communicative person, I really appreciate coming into contact with people from all over the world. The well-being of others is very important to me.“
Peripheral nerve tumors can occur anywhere in the body. Most of them aren't cancerous ...
Vulvodynia is a chronic pain syndrome affecting respectively the vulva and occurs ...
Klausstrasse 4
CH - 8008 Zürich
Switzerland
E-Mail: mail@possover.com
Tel.: +41 44 520 36 00